The Scroll event
Hey ,
I'm thrilled to help you learn JavaScript. Unfortunately, you've landed on a page where you cannot access with your current purchase.
Please upgrade (use this link) access this content.
I'm super eager to help you learn more!
Hey ,
I'm thrilled to help you learn JavaScript. Unfortunately, you've landed on a page where you cannot access with your current purchase.
Please upgrade (use this link) access this content.
I'm super eager to help you learn more!
JavaScript has a scroll event that activates when an element scrolls.
document.addEventListener('scroll', event => {
console.log('Scrolling')
})
You can get the document’s (or window’s) scroll position with these two properties:
window.scrollX: horizontal scroll positionwindow.scrollY: vertical scroll positiondocument.addEventListener('scroll', event => {
console.log(window.scrollY)
})
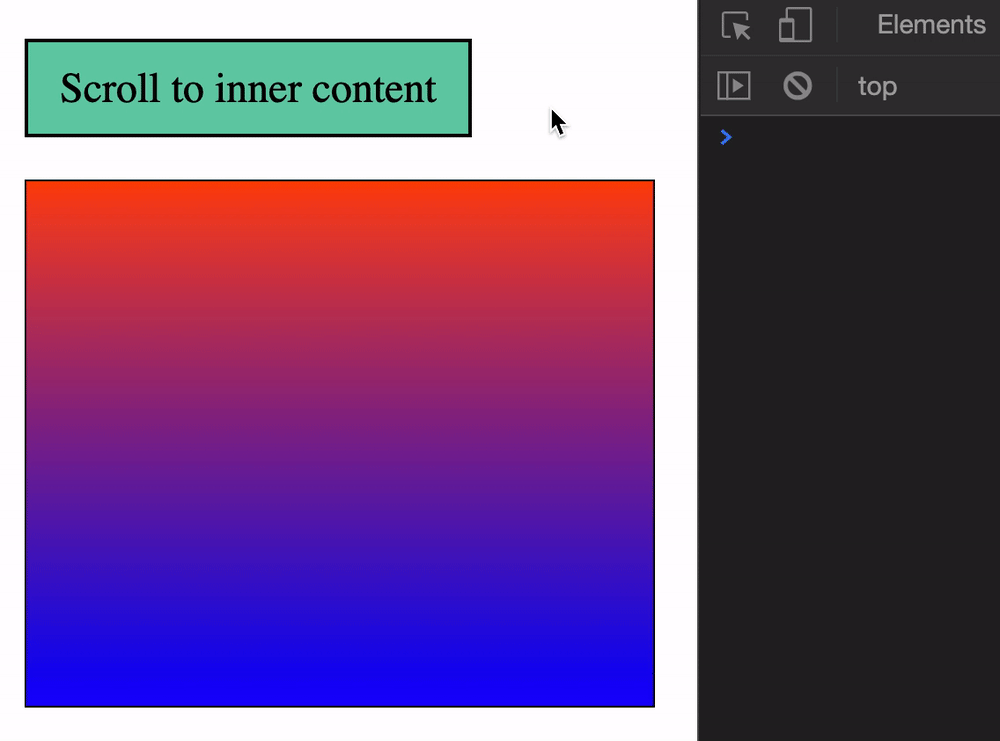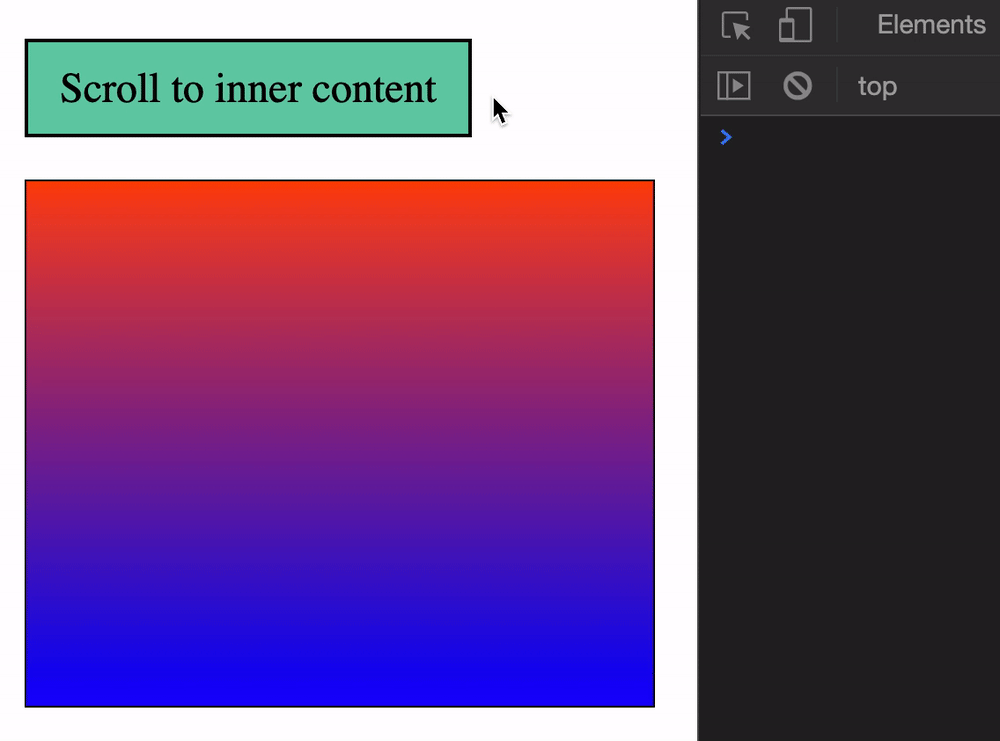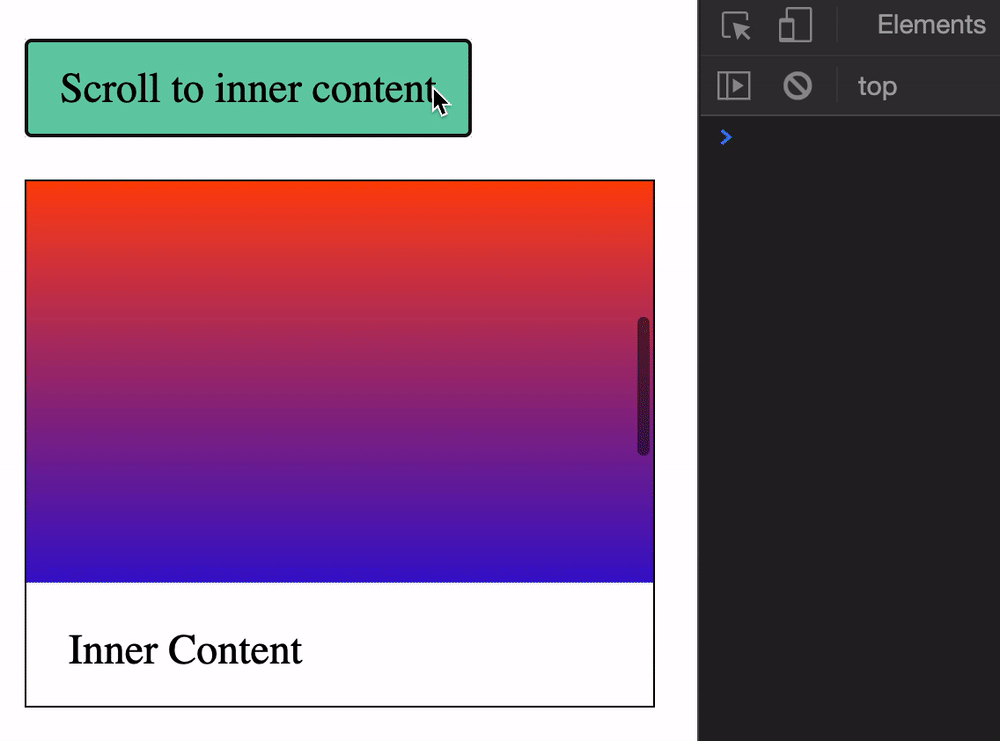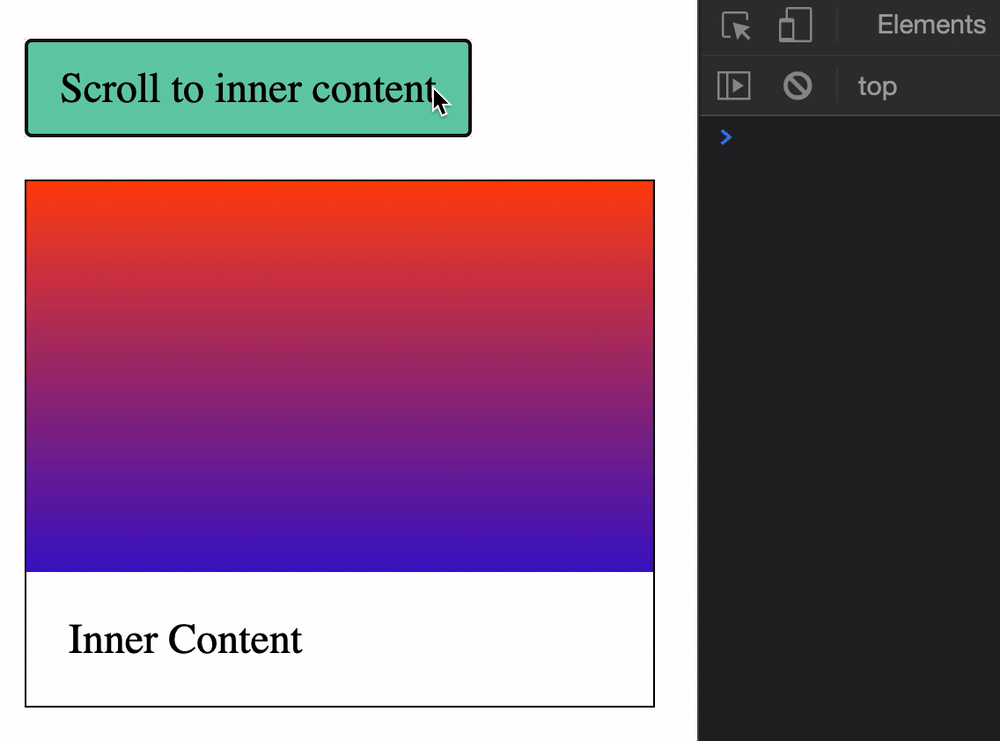
You can get the scroll position of an element with these:
element.scrollLeft: Element’s horizontal scroll positionelement.scrollTop: Element’s vertical scroll positionWe need to create a scrollable HTML element to demonstrate element.scrollTop and element.scrollLeft. A Scrollable HTML element requires three things:
height property.overflow set to auto or scroll.height.<div class="scrollable">
<div> Inner Content </div>
</div>
.scrollable {
overflow: auto;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
/* Places content below the 300px height limit */
.scrollable > div {
margin-top: 500px;
}
const element = document.querySelector('.scrollable')
element.addEventListener('scroll', event => {
console.log(element.scrollTop)
})
You can change the scroll position with the scroll method. It takes in the X (horizontal) and Y (vertical) values you want to scroll to.
window.scroll(x, y)
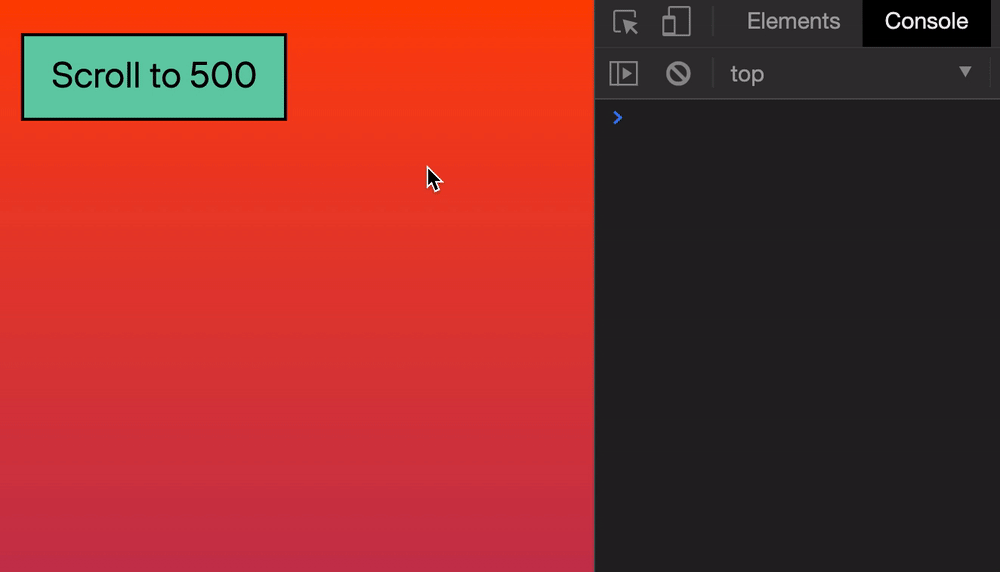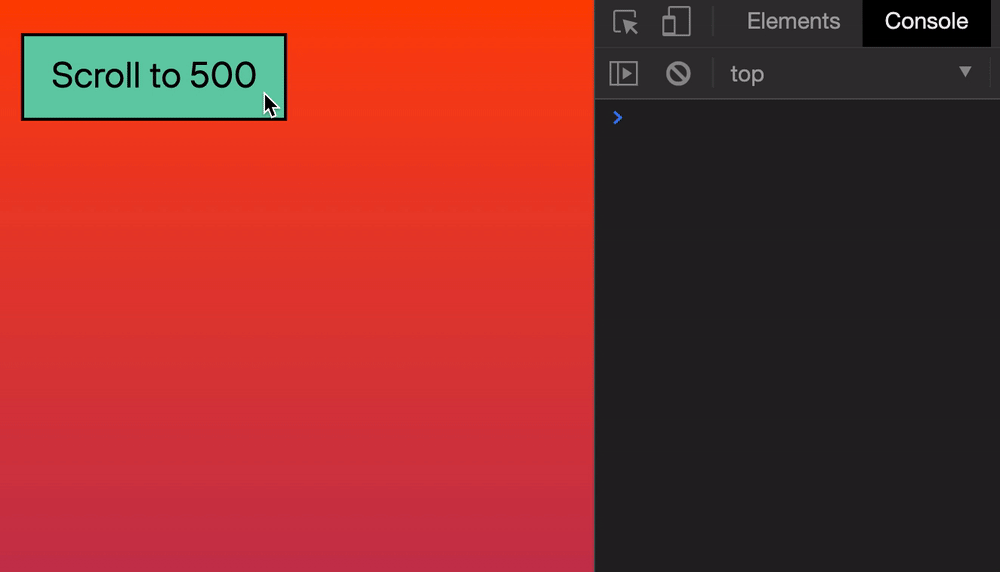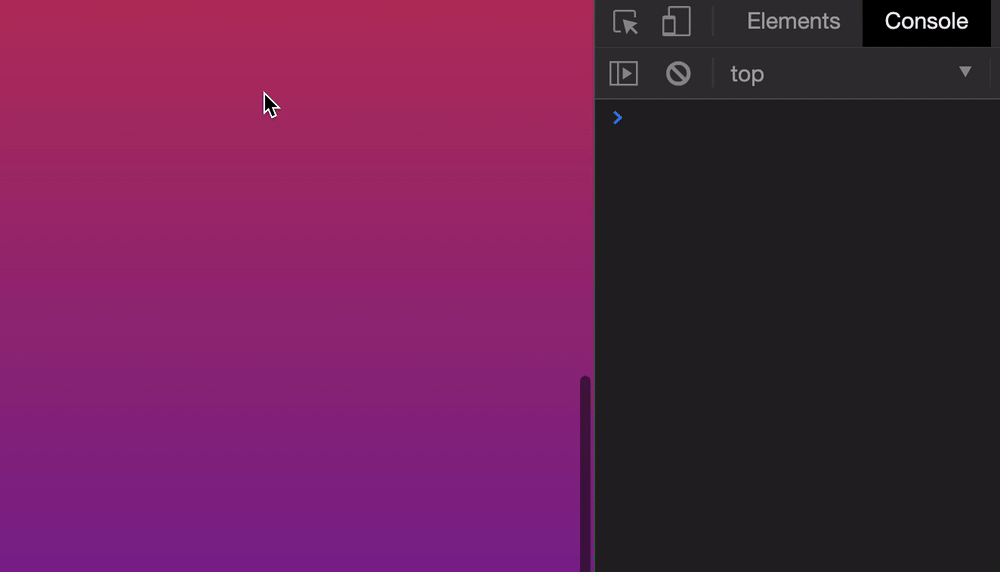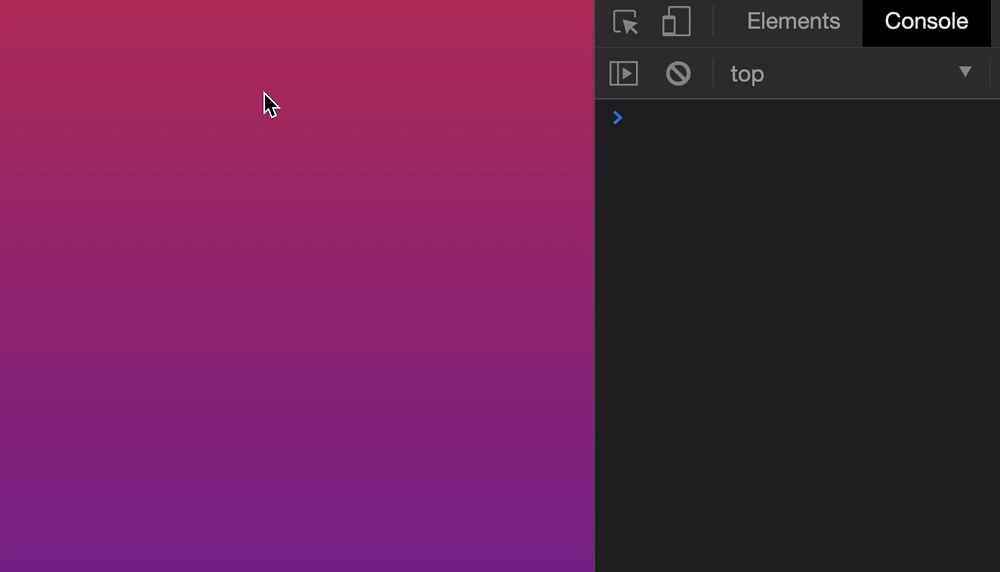
Let’s say we want to scroll the browser’s window to 500px from the top. We can do it this way:
window.scroll(0, 500)
Here’s what it looks like if we click a button to scroll.
const button = document.querySelector('button')
button.addEventListener('click', event => {
window.scroll(0, 500)
})
You can provide an object (instead of X, Y positions) to scroll. This object can have three properties:
left: X positiontop: Y positionbehavior: Whether to jump (auto), or animate downwards (smooth).If you want to animate the scroll position, you need to set behavior to smooth.
const button = document.querySelector('button')
button.addEventListener('click', event => {
window.scroll({
top: 500,
behavior: 'smooth'
})
})
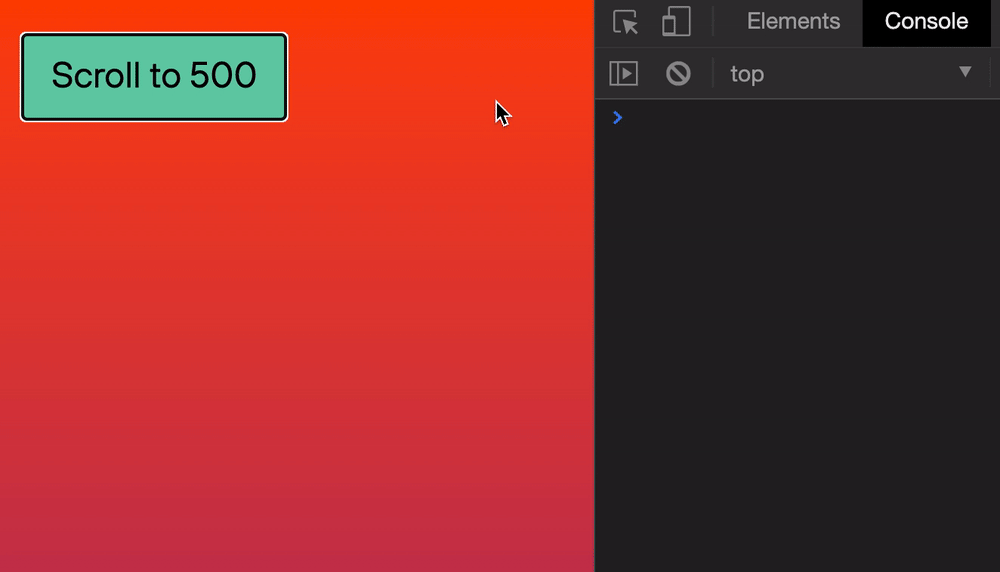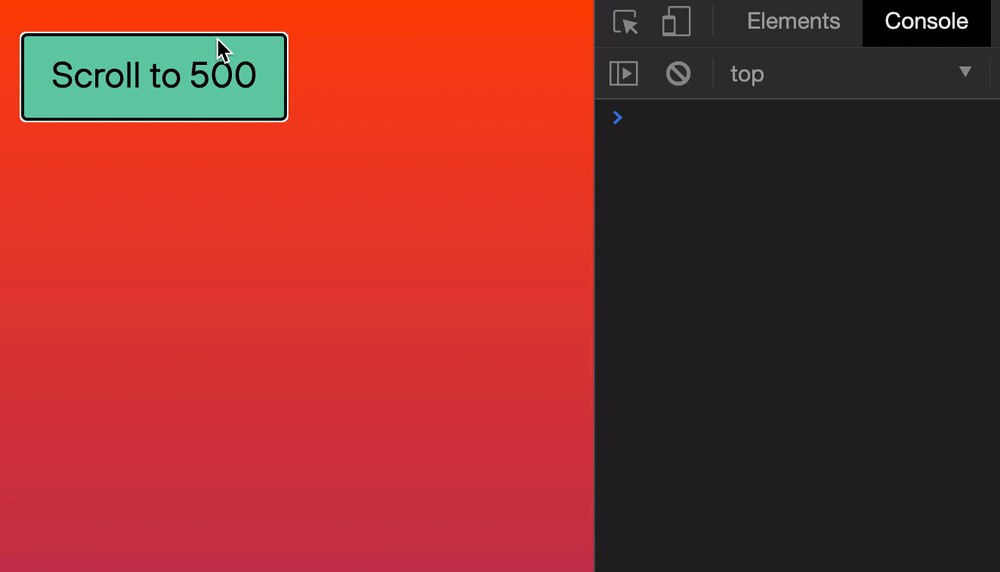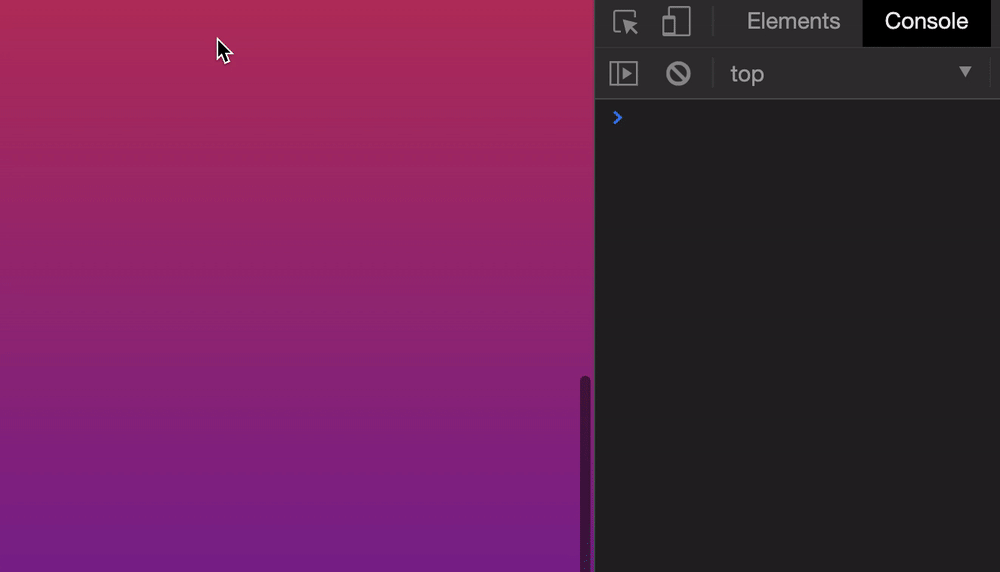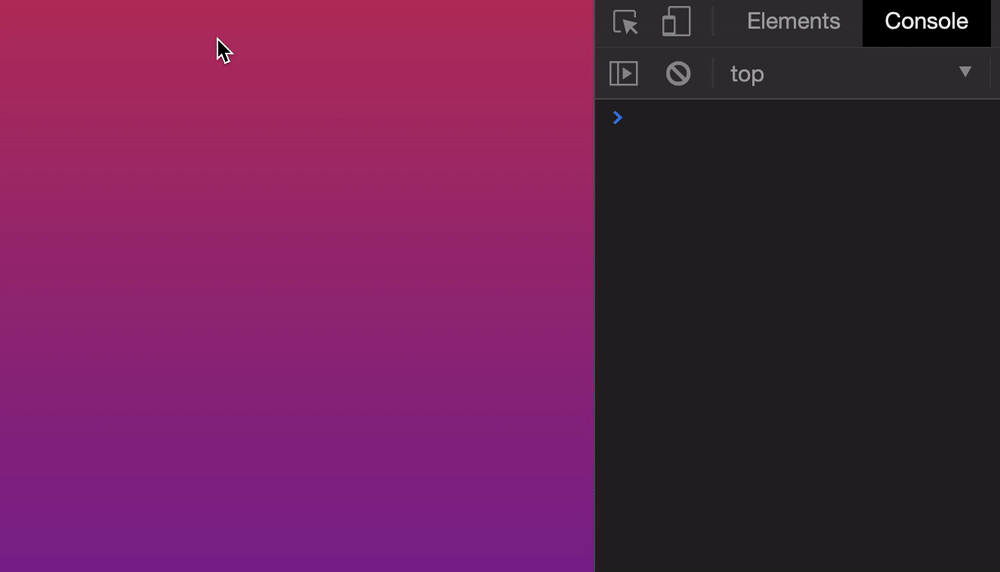
Safari doesn’t support the smooth behavior. It always jumps to the scrolled position.
Note: You cannot set the easing of the smooth behavior. If you want to specify easing, you need to use a library like Green-sock Animation API.
You scroll to a specific position inside an element with scroll as well.
const button = document.querySelector('button')
button.addEventListener('click', event => {
element.scroll({
top: 500,
behavior: 'smooth'
})
})

scrollTo scrolls to a specific position on a page. scrollBy scrolls by a specific number of pixels.
window.scrollBy({
top: 500,
behavior: 'smooth'
});
You can scroll to an element with scrollIntoView. It takes in an object with three options:
behavior: smooth or autoblock: Position of the element you want to scroll to (vertically)inline: Position of the element you want to scroll to (horizontally)element.scrollIntoView(options)
block can take in one of the four values:
start (default)endcenterneareststart scrolls until the top of the target element reaches the top of the scrollable element. (start is a bit wonky. It forces the outer scrollable element to scroll as well).
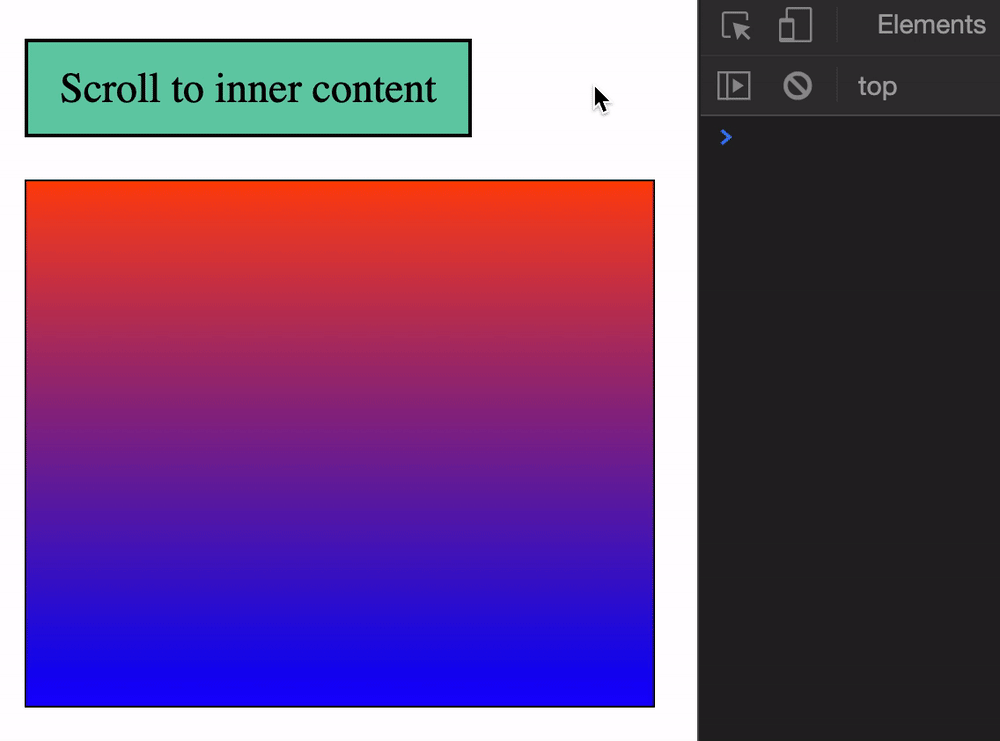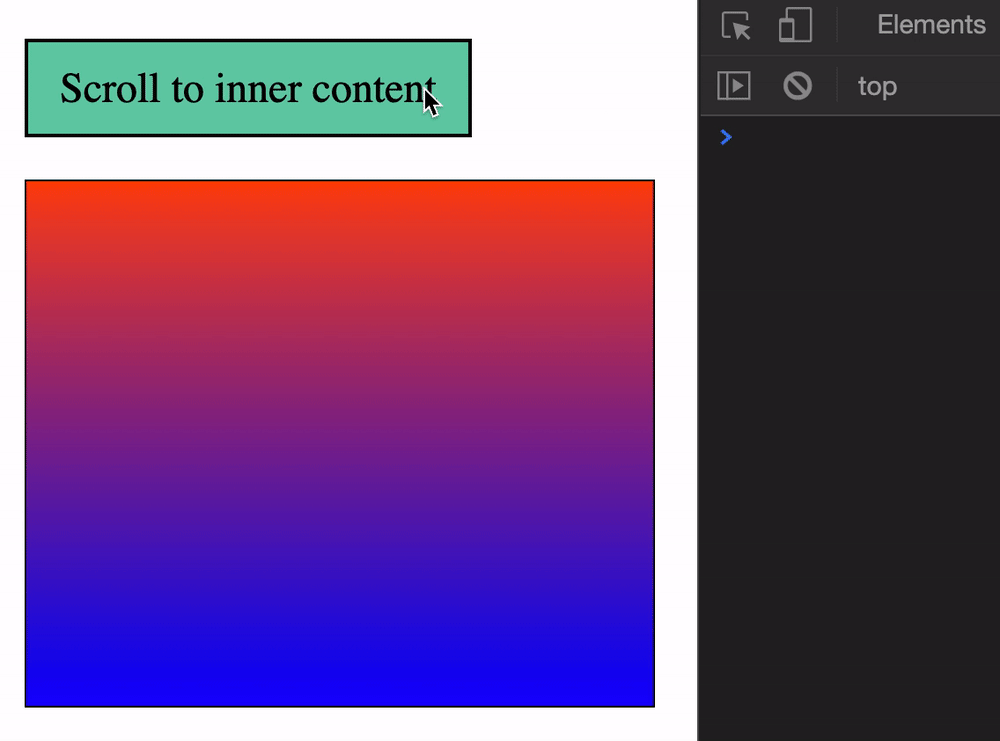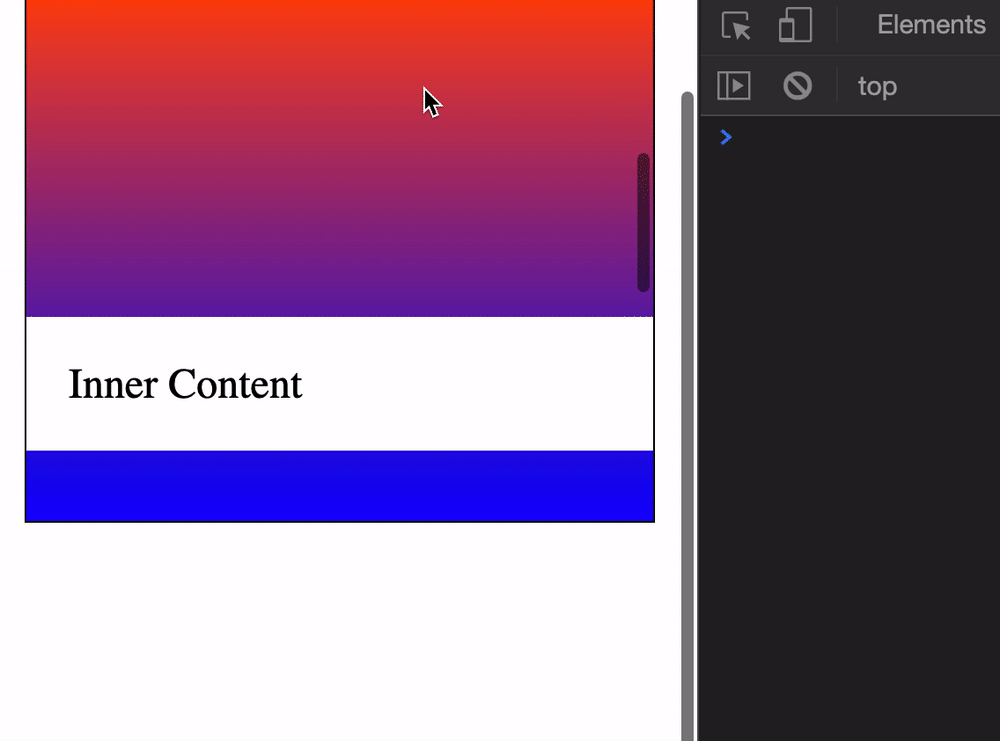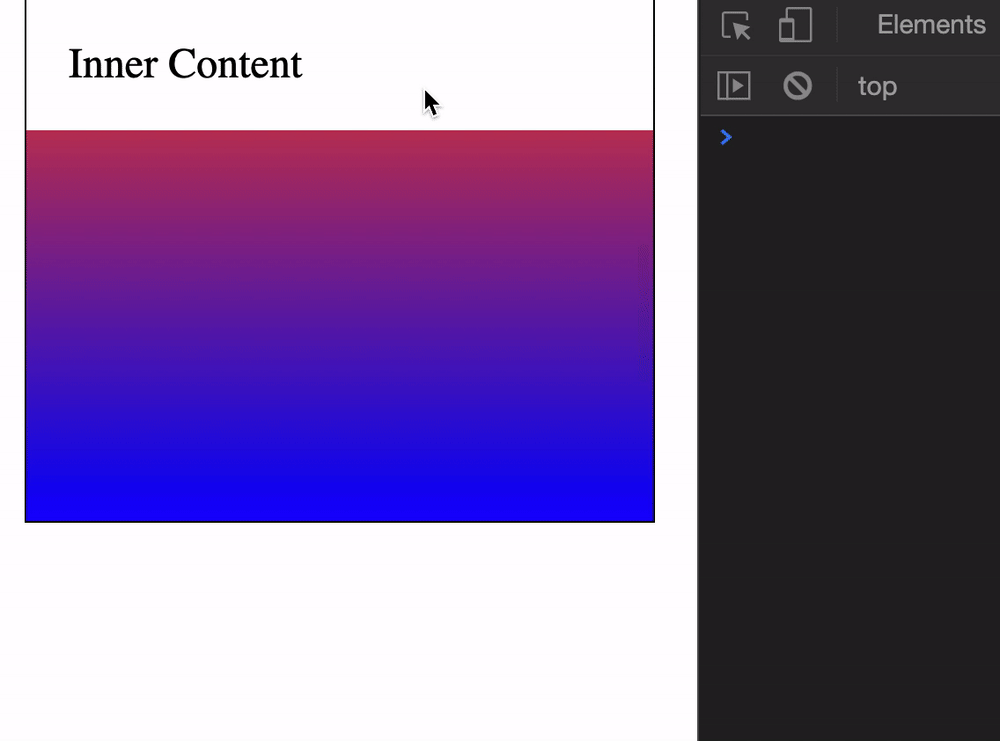
end scrolls until the end of the target element reaches the bottom of the scrollable element.
center scrolls until the target element is in the center of the scrollable element.

nearest scrolls to start or end, depending on which is nearer.

inline takes in the same four values. Substitute left with top, and right with bottom
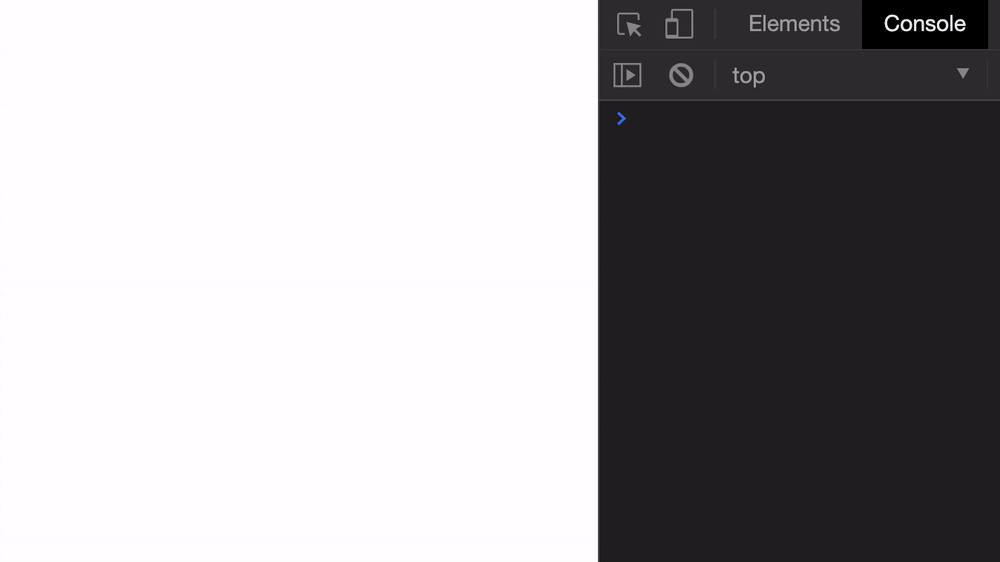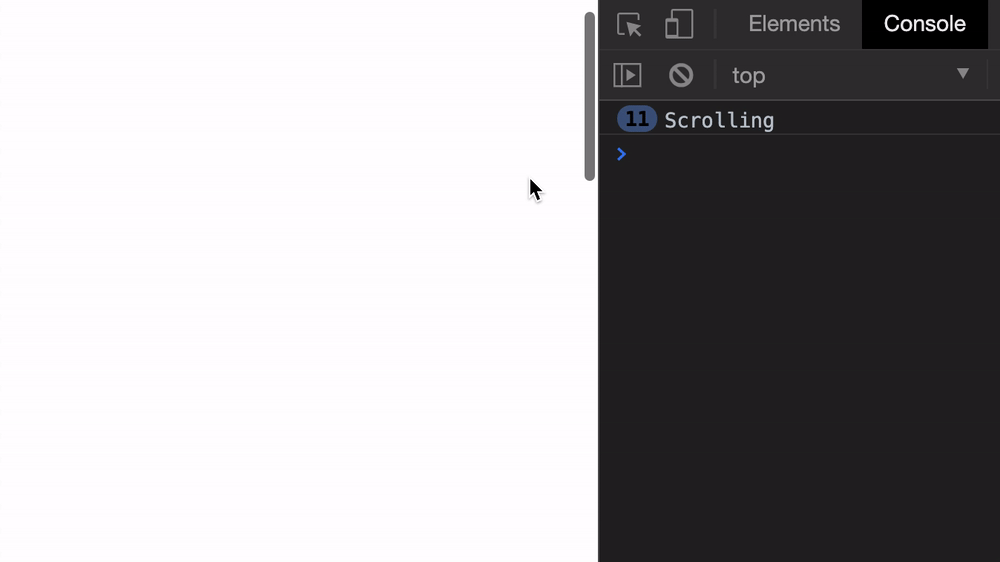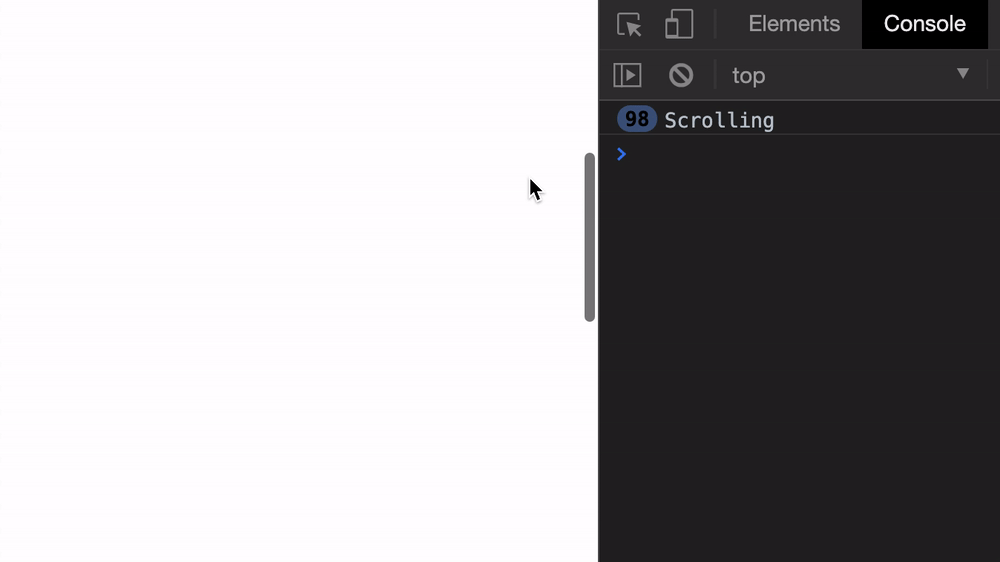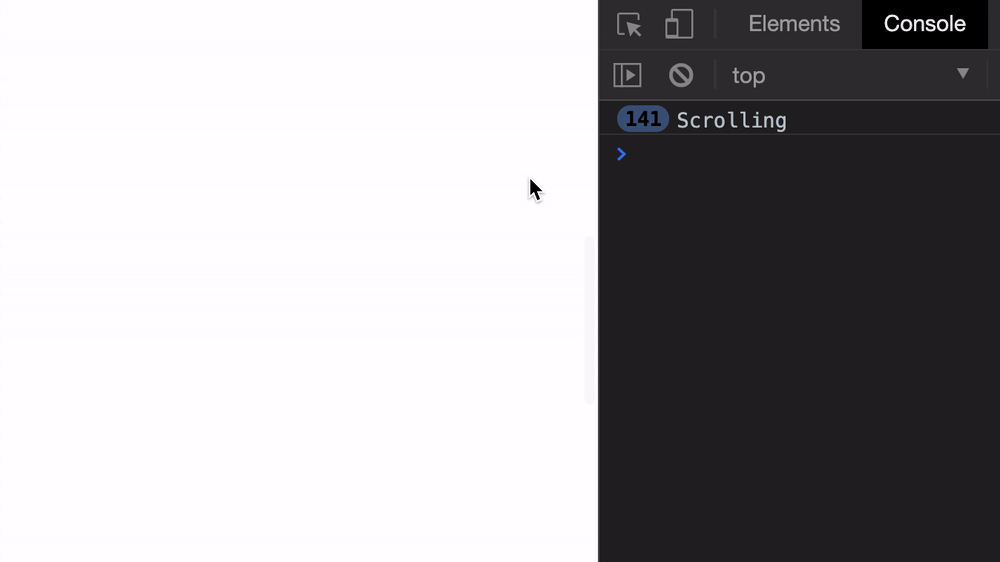
start: Scroll to the left of the elementend: Scroll to the right of the elementcenter: Position the element in the centernearest (default): Scroll to the left or right of the element, depending on which is nearestThe scroll event fires really quickly, as you can see from the GIF below.

Don’t run expensive operations (like changing the DOM with every scroll position) with the scroll event listener. You’ll create jank.